What is Data Breach, What Causes it and How to Prevent it? | Data Breach 2024 Example
What is Data Breach ?
Data Breach Definition
A data breach is a security incident where sensitive or confidential information is accessed or stolen from a system without authorization.
Data Breach vs Security Breach
Data breach is a specific type of security breach, but not all security breaches necessarily involve a data breach.
A security breach broadly refers to any incident that poses a threat to the security of an organization’s system. This includes various types of incidents like unauthorized access, theft, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of data or systems. Whereas a data breach is a more specific type of security breach that focuses on the unauthorized access of data rather than the overall security of systems.
Consequences of Data Breach: How Does it Impact Your Business?
Data breaches result in database leaks that could compromise both the organization and their customers’ sensitive data. The compromised data could include customers’ personal information (names, phone numbers, credit card information leaked, password leak) or the corporate data (intellectual property, employee records, financial records).
The consequences of data breach can be highly damaging, both to SMBs (Small and medium-sized businesses) and large organizations. 46% of cybersecurity breaches worldwide are aimed at SMBs, and especially for these small businesses, the consequences of a data breach can be even more devastating. As they may lack the financial resources and expertise to respond and recover from a data breach, they may end up being forced to entirely shut down due to impacts of the breach. Large businesses would also face significant impacts. Let’s look at how data breaches can damage your business:
- Financial Loss
Your business may incur direct financial losses from investigating the breach, notifying affected parties and implementing security measures such as incident response plans for future prevention. Additionally, there are indirect financial losses resulting from reputational damage, loss of customers, decreased sales and potential legal fees.
According to IBM’s Cost of Data Breach Report 2023, the global average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high of $4.45 million, showing a 2.3% increase from 2022. Organizations that use security AI and automation, however, have been reported to save an average of $1.76 million compared to organizations that don’t.
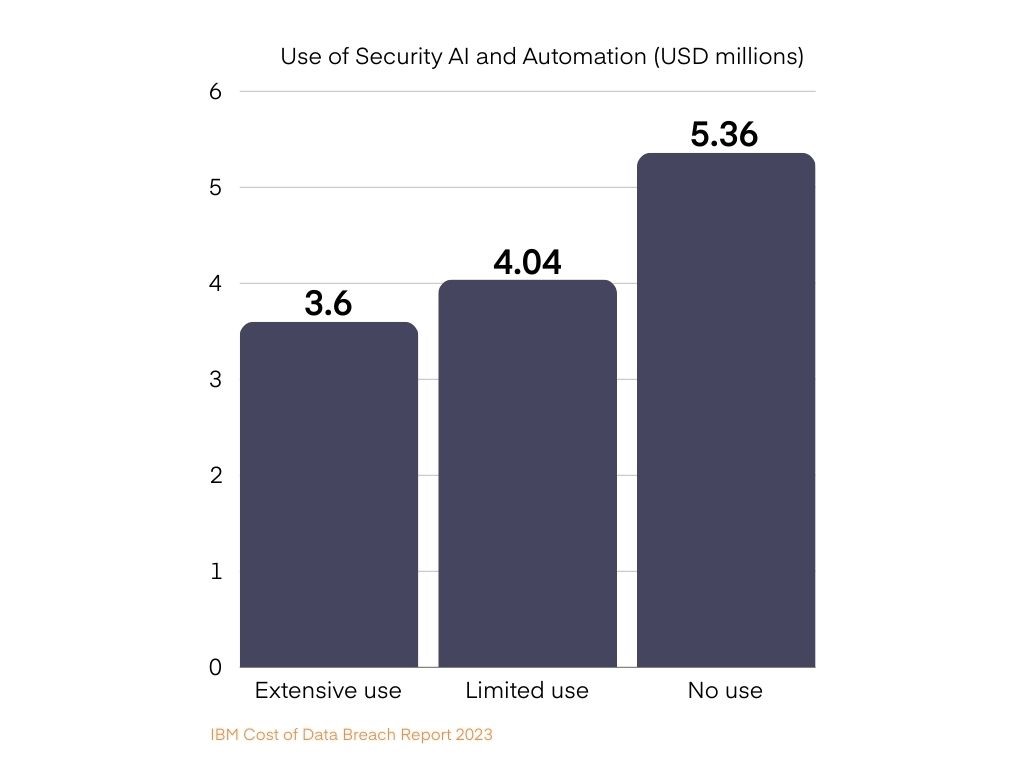

- Reputational Damage
A data breach can severely damage a business’s reputation, breaking customer trust and loyalty. When a company has been breached, customers may lose confidence in the company’s ability to protect their data and choose to leave. Moreover, it could lead to negative word-of-mouth publicity in addition to the already negative media press. This damage to your reputation will make it difficult to rebuild trust, restore the company’s reputation and attract new customers.
A study has shown that in fact, in the US alone, 83% of consumers will stop spending at a business that has been breached, and 21% will never come back to that business again.
- Legal Consequences
Your business may also face legal and regulatory consequences, such as fines, penalties and lawsuits. Depending on the nature of the breach and the applicable laws and regulations (such as GDPR in Europe or HIPAA for healthcare data in the U.S.), your business may be held accountable for failing to protect customer data. Companies must ensure they meet data breach notification law requirements, which require businesses to notify affected individuals about the breach within a specified timeframe.
The biggest fine for data breach is Meta (Facebook) being fined $1.3 billion for violation of the GDPR in 2023. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the world’s most strict data privacy and security law that protects the personal information of the EU population. Meta was fined for transferring personal data from the EU to the US without adequate data privacy protections.
- Operational Disruptions
When your company has been breached, your company’s immediate priority would be to respond promptly to minimize its impact. This, however, disrupts normal business operations as it requires you to divert resources and personnel from regular tasks to this incident response. To add to that, the system downtime, time needed for data recovery and restoration, and supply chain disruption further disrupt normal operations. As a result, some companies may even opt to fully shut down all operations while they focus on recovering from the incident.
Common Causes of Data Breach
Let’s look at some of the common causes of data breach and how they happen in the first place:
- Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks by hackers and cybercriminals are a significant cause of data breaches. These attacks can involve techniques like malware infections, phishing, ransomware, or brute force attacks targeting weaknesses in security defenses.
- Insider Threats
Data breaches can also result from insider threats, where current or former employees or partners compromise sensitive data. This can include actions like unauthorized access, data theft, or negligence in handling sensitive information that leads to the data leak.
- Weak Authentication and Access Controls
Weak or default passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication, and improper user permissions can make it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- System Vulnerabilities
Exploiting vulnerabilities in systems is a common tactic used by hackers, for example injecting malware such as spyware to monitor your keystrokes and secretly collect sensitive data without your knowledge. Failure to promptly patch or update systems to address known vulnerabilities can increase the risk of a data breach. Vulnerability Management Tools like 8iSoft YODA can help your organization identify, assess and remediate vulnerabilities in your systems. These tools scan your system for any security weaknesses such as outdated software or known vulnerabilities and provide insights to help you proactively address any issues before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Third-Party Risks
Data breaches can occur through third-party vendors, suppliers, or service providers that have access to your organization’s systems or data. If these third parties have inadequate security measures, they can expose your sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
To mitigate these risks effectively, organizations can implement third-party risk management (TPRM) tools such as the Alliance TPRM. Tools like Alliance help organizations assess the security posture of their third-party vendors and suppliers.
- Social Engineering
Social engineering is the psychological manipulation of talking a person into revealing sensitive information or granting unauthorized access to systems. Common social engineering techniques include impersonations and phishing through scam emails or text messages. The main goal of these techniques is to trick the target into downloading malware or sharing confidential information.
How to Prevent Data Breach
To prevent breaches, your organization should implement the following best practices of data breach prevention:
- Establish Incident Response Plans
Your company will need to develop an incident response plan to ensure a rapid and effective response to security incidents like data breaches. This Incident Response Plan (IRP) will act as a strategic step-by-step guideline for your organization to know how to manage cyberattacks while minimizing the damage, recovery time and total costs.
- AI and Automation
Companies need security AI and automation to prevent data breaches due to the scale and complexity of modern cybersecurity threats. Traditional methods are often too slow to effectively counteract cyberattacks. AI enables quick, proactive measures to address threats using technologies like anomaly detection and predictive analytics. The 8iSoft YODA Risk Mitigation Platform is an example of a vulnerability management tool that incorporates AI to help your organization identify, mitigate and patch vulnerabilities in real-time.
In addition to saving time, AI also helps your company save money. According to the global 2023 Cost of Data Breach report, businesses using artificial intelligence (AI) and automation were able to save about $1.8 million in data breach expenses. They were also able to speed up the data breach response process by more than 100 days.
- Secure Third-Party Relationships
To prevent any risks of third party breaches, it’s important to evaluate the security practices of your third-party vendors, suppliers, and service providers before engaging with them. Utilizing a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) tool like the Alliance TPRM can help you streamline this process by offering a centralized vendor management, automating risk assessments, and enabling continuous monitoring of third-party vendors’ security performance.
- Train Employees
We have seen how some of the common causes of data breaches include phishing, social engineering and malware. It is thus crucial to provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to employees to raise awareness on these threats, such as how to identify and report suspicious activities or the best practices for data security.
- Implement Strong Access Controls
Limit access to sensitive data only to authorized individuals. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong password policies, password managers and single sign-on (SSO) to ensure that only authenticated users can access sensitive information.
Data Breach Response Plan: What To Do After a Data Breach
A Data Breach Response Plan is essential for organizations to effectively mitigate the impact of a breach and minimize potential damages to sensitive information and reputation. Here’s a guide on creating and implementing a Data Breach Response Plan:
1. Activate the Response Team
Act quickly and immediately assemble your data breach response team comprising of experts from the following areas: IT, legal, public relations, investor relations, human resources and management. Most importantly, to stop further data loss, a data forensics team is required to locate the source of the breach.
2. Detection and Assessment
Implement monitoring tools to thoroughly investigate and detect data breaches as soon as possible. Once a breach is detected, promptly assess the scope and severity of the incident, including the type of data compromised, the extent of unauthorized access, and potential impact on affected individuals and the organization.
3. Containment and Mitigation
To prevent the breach from spreading further, immediately isolate affected systems/servers/networks, reset passwords and change other access credentials. Activate Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block any potential threats in real-time. These systems can help detect and mitigate ongoing attacks before they cause further damage. Identify gaps in your security posture and implement necessary improvements.
4. Notify Relevant Stakeholders
Notify affected individuals (customers, employees), regulatory authorities and law enforcement agencies. Communicate transparently and promptly about the breach, its potential impact, and the steps being taken to address it. Provide guidance and support to affected individuals on how to protect themselves from potential harm.
Latest Data Breach Example: Data Breach 2024
Data breaches have become increasingly common, with organizations across various industries facing the constant threat of cyberattacks. Despite advancements in security measures, cyber attackers continue to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. For example, recently in 2024 an alarming breach incident had occurred to Dell Technologies:
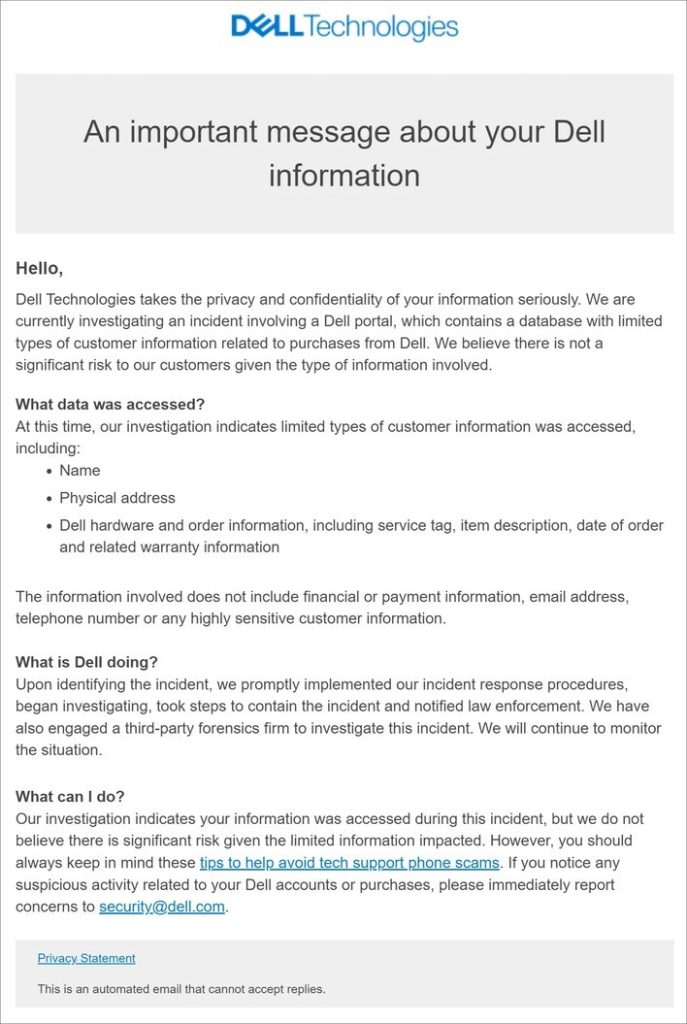
- What happened? Technology giant Dell has been breached by a hacker who has stolen access to Dell’s database of purchase records from 2017 to 2024. The hacker has listed the stolen data for sale on the Breached hacking forum. The stolen data included sensitive information such as full names, addresses, service tags, shipping dates, warranty plans, serial numbers and Dell customer/order numbers.
- What caused it? The hacker was able to access the database through a loophole in Dell’s partner registration process. By registering multiple accounts under fake company names, the hacker gained access to the Dell portal for partners, resellers, and retailers, that could be used to look up order information without verification.
- Impact: Even though Dell mentioned that the breach does not include highly sensitive data such as financial information, the hacker could still use the collected information for malicious activities such as phishing. For example, the hacker could use the address, serial number and order information to send USBs containing malware and trick people into installing this malware. Due to this data breach incident, customers could lose trust in Dell products as they have become a “technology company that has been hacked.”
- Response: Dell has notified customers of the data breach through email, informing them what type of data has been exposed, what the company is doing to mitigate the breach, and offering guidance on what customers can do in response to this incident. The company also emphasized that no critical customer data such as sensitive personal or financial information was compromised.

The Dell Data Breach 2024 incident serves as another reminder that even well-established companies are vulnerable to cyberattacks, highlighting the constant need for robust cybersecurity measures.
